Inverter (logic gate)
Electronic implementation
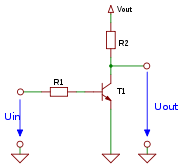
An inverter circuit outputs a voltage representing the opposite logic-level to its input. Its main function is to invert the input signal applied. If the applied input is low then the output becomes high and vice versa. Inverters can be constructed using a single NMOS transistor or a single PMOS transistor coupled with a resistor. Since this 'resistive-drain' approach uses only a single type of transistor, it can be fabricated at low cost. However, because current flows through the resistor in one of the two states, the resistive-drain configuration is disadvantaged for power consumption and processing speed. Alternatively, inverters can be constructed using two complementary transistors in a CMOS configuration. This configuration greatly reduces power consumption since one of the transistors is always off in both logic states.[1] Processing speed can also be improved due to the relatively low resistance compared to the NMOS-only or PMOS-only type devices. Inverters can also be constructed with bipolar junction transistors (BJT) in either a resistor–transistor logic (RTL) or a transistor–transistor logic (TTL) configuration.
Digital electronics circuits operate at fixed voltage levels corresponding to a logical 0 or 1 (see binary). An inverter circuit serves as the basic logic gate to swap between those two voltage levels. Implementation determines the actual voltage, but common levels include (0, +5V) for TTL circuits.
Digital building block
The inverter is a basic building block in digital electronics. Multiplexers, decoders, state machines, and other sophisticated digital devices may use inverters.
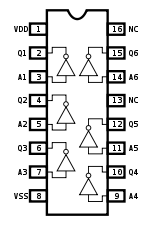
The hex inverter is an integrated circuit that contains six (hexa-) inverters. For example, the 7404 TTL chip which has 14 pins and the 4049 CMOS chip which has 16 pins, 2 of which are used for power/referencing, and 12 of which are used by the inputs and outputs of the six inverters (the 4049 has 2 pins with no connection).
Analytical representation
{\displaystyle f(a)=1-a} {\displaystyle f(a)=1-a} is the analytical representation of NOT gate:
{\displaystyle f(0)=1-0=1} {\displaystyle f(0)=1-0=1}
{\displaystyle f(1)=1-1=0} {\displaystyle f(1)=1-1=0}
Alternatives
Further information: NAND logic and NOR logic
If no specific NOT gates are available, one can be made from the universal NAND or NOR gates.[2]